
What is Authentication:
So before going deep into two-factor authentication, let’s talk about authentication first. It’s a process of confirming that you are yourself and not someone else trying to pretend to be you. Example: The system allows you to log in only on your account, not somebody else. There are two types of authentication. One-factor authentication and Two-factor authentication.

1. What is One-factor authentication
This is the most common authentication method: you enter your username and password—the software checks whether there are such usernames and passwords in the database. If so, it recognizes you. Then it looks to see if you have certain operation permission in the system.
The system doesn’t care who exactly enters the username and password. The main thing is that they match with the database. So if an attacker spies on us entering a username and password from some forum, then they can log in on our behalf to do evil.
If you remember your username and password, you’ll be able to log in relatively quickly. If someone else finds out your username and password, they will get into the software under your name. People often use an email address as their username — This is public information, and it is easy to calculate.
People don’t often use many different passwords for different services. So if one service leaks your password, attackers will be able to use it in other services as well.
The password is often the date of birth, which can also be public information.

(Photo Source: safetydetectives.com )
2. What is Two-factor authentication & how does it works
The system uses two unrelated authentication methods for two-factor authentication (also known as 2FA). The first one is normal (username/email + password), and the second is extra security.
The second method must be independent: on a different device or using a fundamentally different method. The calculation is designed to significantly complicate the life of intruders who may want to use someone else’s username and password.
Two-factor auth sometimes makes login to a service bit longer. But for all good reason.
Reliability above: To log in on your behalf, you need to access your phone or mail inbox. Plus, you need to know their passwords. It is difficult to break in, even if you have the same password everywhere.
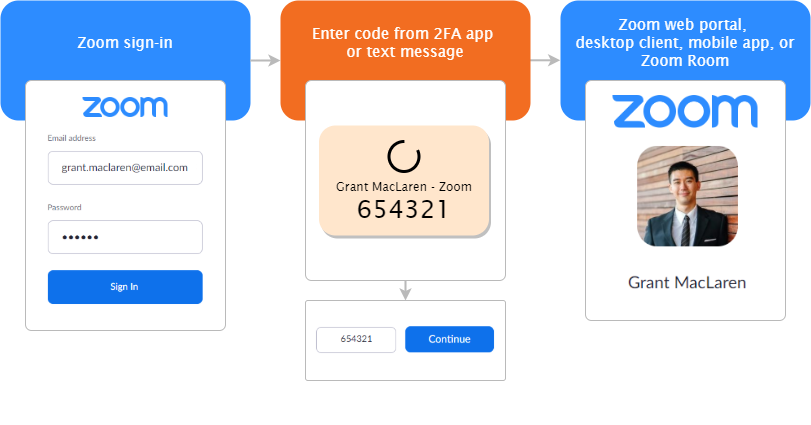
(Photo Source: Zoom.us)
Types of Two-factor authentication
SMS code with confirmation.
It is assumed that a person does not share their phone number with other people, so they will read it if you send them an SMS. This is how almost all online banks work. You can also send the code to your email address or app. The meaning is the same.

(Image Source: smstools.com)
Link to your email address.
After the login and password, the system sends a unique one-time link, after clicking on which the system makes sure that you are you. Unfortunately, it’s not very secure because email is easy to hack

Confirmation in the app.
If the service has an app and you have installed it, the service can contact the app on your phone and ask you a question there: “Are you logging in?”. Logging into a Google account, for example, works like this.

An authenticator app with a code.
For more complex scenarios, there are particular applications — for example, Twilio Authy. The server and your application agree on some cryptographic algorithm. When you need to enter the second code, you don’t see it in a text message but in the app.
This method is used for logging in to some email services or secure contours of corporate networks. For example, you can set your OTP for Gmail, Twitch, and Snapchat with Authy. This type of app-based OTP generation is also called TOTP or Time Based OTP. It is much more secure than traditional email or SMS-based OTP.
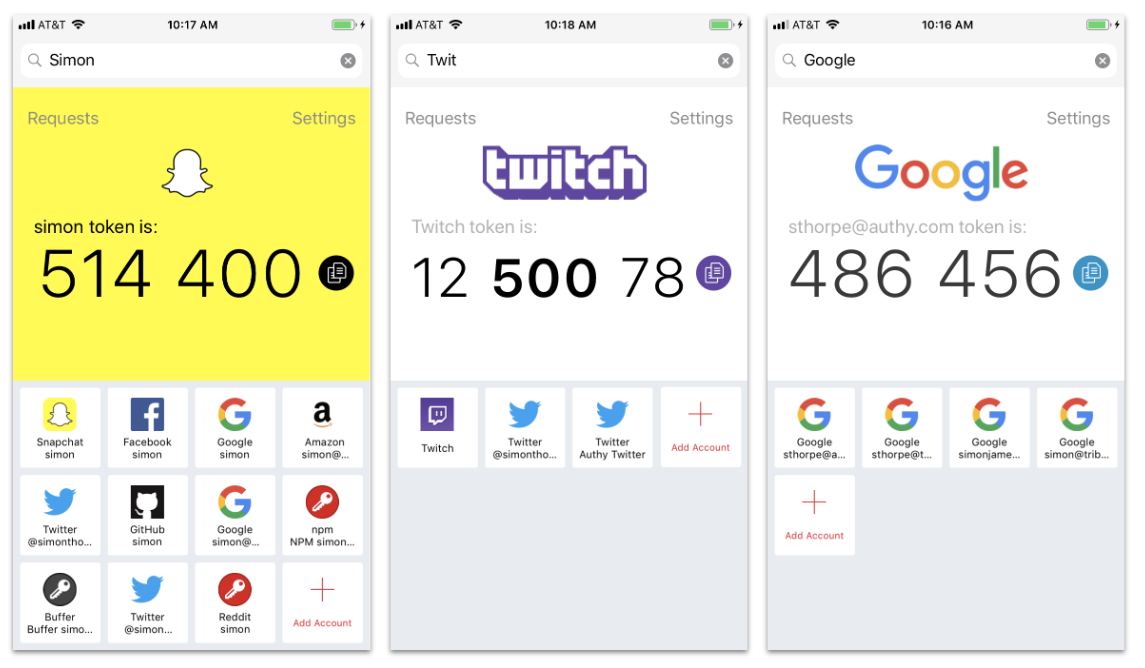
QR code authentication.
The app may have a “Read QR code” function: hold the camera up to your computer, and the system makes sure that you are the one sitting in front of the screen.
This is how authentication works for the web version of WhatsApp or Telegram Web.

Pro-Life Tips: DO NOT scan a freaking random QR code from the internet. You might become a cybercrime victim.
Authenticator device.
Usually, they are made in the form of a flash drive with a button and a screen. Click on the button, and the code is displayed. If the flash drive is lost — you will need to go to the person who issued it. Without this, the system will not let you go anywhere just by using your username and password.

USB token.
It also looks like a flash drive, but inside there is a special chip and cryptosoft. This software securely connects to the system and enters the necessary access code that the chip generates for it. If you lose it, access will also be lost.
By itself, it is useless — you need to link it to the authentication system of your software so that they know about each other. If you only buy this token, its codes will not reveal anything to you.
NFC card or magnetic tape card.
Sometimes bank employees have a special card reader connected to their computer. To perform an important operation, the employee must confirm it with their bank card: they say, it’s definitely me.
Biometrics.
Biometrics is everything that concerns your body: recognition of fingerprints, face, voice, biorhythms, aura, and whatever else they come up with. As a rule, it is used on large and important objects with high-security requirements.
Security rules for two-factor authentication
-
Take care of your mobile phone.
-
If you can enable two-factor authentication in the system, service, or app, enable it.
-
If you can use two SIM cards — use them. Send SMS codes to a second SIM card that doesn’t show up on ad sites, forums, or other people’s notebooks.
-
It is better to have a spare email address that you don’t see anywhere else so that you can use it to log in to important services.
-
If the app has a PIN code, don’t put someone’s date of birth on it.
-
Don’t use the same password everywhere.
-
Download apps only from the official app store. In the unofficial ones, you can find all sorts of abominations that can intercept your codes.
What is TOTP
TOTP stands for Time-based One-Time Passwords. It is a common method of using 2FA in applications. Unique numeric passwords are generated that use time as a deciding factor. The time-based passwords are available offline and provide user-friendly functionality for 2FA.

Image Source: Twilio.com
The TOTP algorithm uses a form of symmetric key cryptography: the same key is used by both parties to generate and validate the token.
Why should you use TOTP, not SMS based OTP
TL;DR Please don’t use SMS-based OTP.
Look, SMS can be hacked. It is extremely backdated, has no encryption, and your telco stores all of your messages for years. Also, you never know what apps you have on your phone (Like Pegasus ).
The Google Play Store and the Apple App Store do some scanning to prevent malware from publishing in the store. However, these security scans often have pitfalls that let malicious apps pass through.
Both legitimate apps and malware can use an OTP interception mechanism. As a result, it can pass stores’ standard security checks successfully.
Did you ever notice that some apps send you SMS OTP and automatically fill it for you while signing up? Who said that is limited to only legit apps?

How does a malicious app intercept OTP
An OTP interception only requires two permissions, and one of them (Internet access) is a very common one. Consequently, apps featuring OTP interception for a malicious purpose do not appear suspicious at first sight.
-
Permission to intercept SMS: ‘android.permission.RECEIVE_SMS’
-
Permission to send the content, using internet or an SMS: ‘android.permission.INTERNET’ or ‘android.permission.SEND_SMS’
You can see how easy it is for an attacker to intercept your SMS-based OTP. Heck, there are lots of bots that can intercept the SMS OTP. The bots are very effective and easy to use. Even some bots have an 80% efficacy rate. These bots are designed to trick users into revealing the OTP sent via SMS. A new bot called “SMSRanger” is straightforward to use and one of the most popular bots available. As Intel471 reports:
“Those who pay for access can use the bot by entering commands similar to how bots are used on popular workforce collaboration tool Slack. For example, a simple slash command allows a user to enable various ‘modes’ — scripts aimed at various services — targeting specific banks and PayPal, Google Pay, Banking apps, or carriers.
The bots need only the phone number of the victim. Then it does the rest to gain access to the targeted account. SMSRanger has an efficacy rate of 80%; if the victim answered the call and the provided the updated and accurate information.”
Apart from these, TOTP has several benefits, including:
- Offline support
- Easy configuration
- Standardized authentication solution
- Software-based, not dependent on carrier fees or telephony access and deliverability
- Faster average time to authenticate
- Increased security compared to SMS 2FA: the secret key input for TOTP is only shared once, and the method does not rely on the telephony network, which helps reduce the attack surface.
- TOTP has stronger proof of possession than SMS, which can be legitimately accessed via multiple devices and may be susceptible to SIM swap attacks.

In this article, we discussed what two-factor authentication is, how it works, and why you need it. We also discussed different types of 2FA methods, security rules, and risks of using SMS-based OTP. I hope it will help you make your online life a little safer.

