Meet Lil Michelu. She has more than 3 million followers on Instagram, starred in a Calvin Klein ad campaign with Bella Hadid, and according to Time magazine, she is one of the 25 most influential people on the Internet. Lil Miquela has all the makings of an Instagram teen queen, from the effortless good looks to the philosophical selfie captions (“You can be not okay and still be strong”). She appeared in an issue of V Magazine, which dubbed her the “face of new-age logomania” (a reference to the gear she “wears,” from brands such as Balenciaga and Kenzo). And in June, she was featured in Wonderland’s summer issue—alongside actual celebrities like Migos and Amandla Stenberg.
Just one issue. She DOES NOT exist in real life.
Also, there are no virtual Gucci sneakers on sale for $ 17.99 or the most expensive NFT art that was sold for USD 91.8 million.
It seems that more and more aspects of our lives are being overtaken by digitalisation. Whether this is good or bad is up to you, but it is what it is. Let’s explore.
Following topics are covered in this article
- How the Web developed
- What Metaverse mean for developers and the IT industry
- What is Web3
- What is Metaverse
- Implications for the Crypto Industry
- The international potential of Metaverse
- Political and economic risk factors
- Metaverse regulation
- What the Metaverse mean to you and me
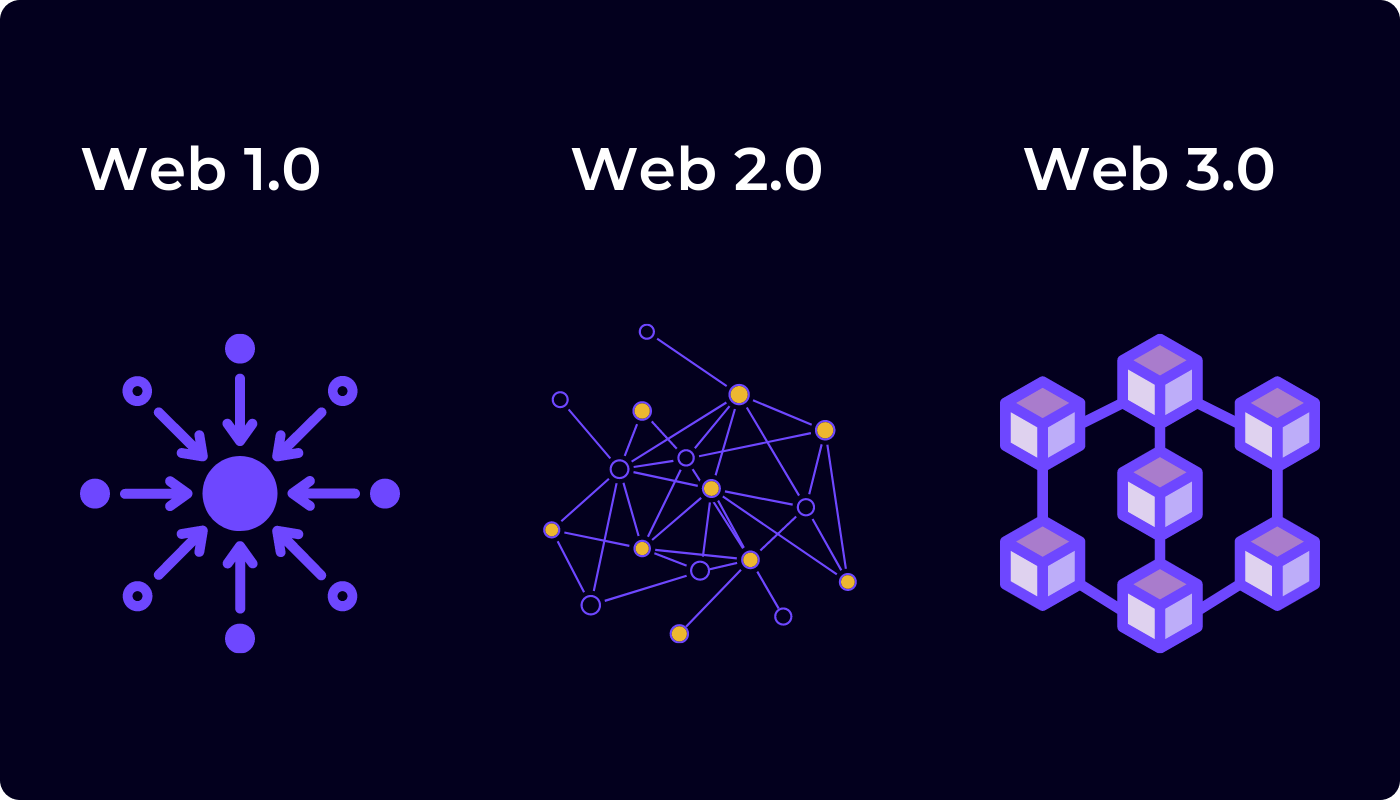
How the Web developed
Stages of Internet development over three decades:
-
Web 1.0-companies create content, users consume it, and profit from advertising sales
-
Web 2.0 - large corporations (Facebook, Amazon, etc.) have entered the game, users consume and create content that corporations profit from.
-
Web 3.0 - users collectively own what they create and earn, as well as create virtual spaces and applications that belong to the community (for example, Decentraland)

Web 2.0, conceived by O’Reilly and others between 1999 and 2004, moved the world from static desktop web pages designed for information consumption and served from expensive servers to the interactive experience and user-generated content that Uber, Airbnb, Facebook, and Instagram brought us.
There is a transition from a closed and centralised Web 2.0 to an open Web 3.0, mainly managed by users, not by large technology companies. Web 3.0 has become the first stage in the development of an Internet, where user can monetise their activities without intermediaries and interact at a new level.

What is Web3 ?
According to Wikipedia
Web3 (also known as Web 3.0 and sometimes stylized as web3 is an idea for a new iteration of the World Wide Web based on blockchain technology, which incorporates concepts including decentralization and token-based economics. Some technologists and journalists have contrasted it with Web 2.0, wherein they say data and content are centralized in a small group of companies sometimes referred to as “Big Tech”. The term was coined in 2014 by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood, and the idea gained interest in 2021 from cryptocurrency enthusiasts, large technology companies, and venture capital firms.
What Is The Metaverse?
The term ‘metaverse’ is a buzz word that combines ‘meta’ and ‘universe.’ It is used to refer to an anticipated future iteration of the internet which currently we call WEB 3.0. This evolution of the internet is expected to see the rise of online 3-D or virtually integrated environments that provide users access to virtual reality and augmented reality experiences.
The metaverse is expected to transform the tech world, where companies will be creating the architectures, and software that will power the metaverse version of Web 3.0. But it will also affect companies outside the technology sphere. Metaverse is trying to change even simple things like how people shop for groceries, navigating to destination, buy products, and interact with ads as a consumer.
What Metaverse mean for developers and the IT industry
And again, developers will get all the attention because creating a metaverse is impossible without them. The development approach will be more like developing games or “experiences” for virtual systems (Oculus Quest and HTC Vive), virtual worlds (Roblox and Fortnite), game consoles (Playstation and Xbox), and the Internet itself. And the main question is how to combine the digital world with the real one. We will soon be able to get answer from Microsoft, Nvidia with their Omniverse, and Facebook (now called Meta) with it’s Metaverse.

The metaverse is a new infrastructure level created as the digital and physical worlds converge. The merger will give more scope to developers; in Metaverse, they will be able to realise their creative and technical potential because all objects of the digital world are lines of code. I think they open up tremendous opportunities. The metaverse is where we will start using cryptocurrencies instead of money. Satya Nadella Microsoft CEO, Build Conference, June 2021
Implications for the Crypto Industry
Metaverse will become a driver of the growth of the digital asset industry and will contribute to the mass adoption of cryptocurrencies as a payment instrument. This was stated by Bank of America investment strategist Chaim Israel in a conversation with Business Insider.
I think they open up tremendous opportunities. The metaverse is where we will start using cryptocurrencies instead of money.
Israel clarified that the volatility of existing cryptocurrencies would not allow them to become the dominant means of settlement. In his opinion, this role will be played by stablecoins tied to the value of fiat assets.
But many people will want to argue with this because true adherents of decentralisation believe that centralised stablecoins should be abandoned to build a full-fledged digital economy. Moreover, now in El Salvador, you can pay with bitcoin for a burger at McDonald’s or send an instant transfer to a bitcoin wallet instead of sending it via Western Union.

Earlier, Grayscale Investments predicted an increase in the Web 3.0 metaverse sector’s annual revenue to $1 trillion. Experts noted that virtual world platforms integrated with cryptocurrencies, DeFi applications, NFT, decentralised management and cloud storage create new ways of interaction that attract users.
The international potential of Metaverse
The metaverse can foster the development of virtual communities, networks, and economies that transcend borders and national identities. One day, people may identify primarily with decentralised autonomous organisations based on the metaverse, with quasi-foreign policies. Such a transition may require rethinking geopolitical affairs from scratch. This can be both a threat and an incentive for developing and forming new foundations.
The metaverse can potentially change the world for the better by introducing international virtual embassies, which will help developing countries be on an equal footing, improve awareness, and make it easier to form alliances that were previously unlikely due to lack of resources.
Political and economic risk factors
While the metaverse can revolutionise work and entertainment concepts, it is essential not to forget the dangers if it affects everyday life. For example, increasing digital espionage.
Virtual environments will strengthen disinformation, espionage, and surveillance campaigns. The struggle for control over the physical infrastructure of the metaverse may well lead to an aggravation of global conflicts. And the supranational nature of the metaverse, where the boundaries of the natural world become much less relevant, can also revolutionise the way people perceive and interact with nation-states.
Do not be afraid and take it literally: it won’t happen tomorrow or even the day after. But still, there is already evidence that online multiplayer games can contribute to the spread of misinformation and conspiracy theories. Players can use in-game communication tools to spread rumours or “fake news”. Just be more careful when choosing content for consumption and communities for communication.
The countries that will maintain and provide the physical resources to sustain the Metaverse will significantly influence the digital field. Countries that have control over technologies determine the direction of development of these technologies and accumulate capital. These factors combine to provide significant international leverage, which will cause global inequality. So, for example, China with the Digital Silk Road system and Taiwan, which dominates the semiconductor industry, can become the most important market players in the concept of the metaverse. If people continue to own property, earn a living, and maintain social status within the metaverse. A lack of equipment or service disruptions can endanger their livelihoods or undermine social stability. Your whole life will be turned upside down by the slightest network failure: whether it’s a forced power outage or hacker attacks. In theory, Metaverse can open the way to spread destructive content. But there are prerequisites for so-called community moderation: when community members vote for or against content, statements, or messages. In other words, the community can censor objectively destructive content, despite decentralisation.
Metaverse regulation
Metaverse are seemingly easy to regulate – using rules and user conventions. These rules are no different from those we currently accept before launching a game or registering on the site. But given that virtual worlds are built primarily on top of blockchains, they inherit all data security and encryption aspects. And if the Metaverse belong to a community, that is, a massive number of depersonalised addresses that interact with each other, then it will be more difficult to regulate such structures. It’s like trying to force a person to do something they don’t want to do. We’ll have to find a compromise.
Can the state influence Metaverse?
Yes, it can. If Metaverse or their users systematically violate the public interest or the interests of a particular group of people. The simplest example is that Metaverse will have to comply with the law on personal data, and otherwise, they may be blocked, and administrators may be fined.
If Metaverse gain popularity, restrictions will appear. For example, you can limit the maximum time you can spend in the metaverse. There are already time limits for video games for minors in China: one hour on Friday, Saturday and Sunday, and on public holidays.
 Also, the Metaverse may be subject to labour laws, at least in terms of working hours; in the metaverse, it will be impossible to “work”, for example, more than 40 hours a week. But how this will be monitored, provided that authorisation in such spaces will take place using “depersonalized” crypto wallets, is not clear.
Also, the Metaverse may be subject to labour laws, at least in terms of working hours; in the metaverse, it will be impossible to “work”, for example, more than 40 hours a week. But how this will be monitored, provided that authorisation in such spaces will take place using “depersonalized” crypto wallets, is not clear.
What the Metaverse mean to you and me
Meta (formerly Facebook) suggested that the metaverse is a big shared project created by people from all over the world, which will help us take education, professional activities and simple human communication to a new level that was previously inaccessible. Technologies will serve as assistants in this process.
I have collected some ideas that will help you understand what we should expect from the Metaverse:
-
You will be able to explore the virtual world using a device with Internet access while enjoying three-dimensional graphics and sound. VR adds a sense of real presence to the metaverse.
-
The metaverse is social – there are many other people, or rather their avatars. Some of these avatars may be bots, virtual agents, or artificial intelligence manifestations, and you can interact with them. Metaverse proponents and researchers believe that communication can be more natural than video communication because you can use your eyes, facial expressions, and even actions.
-
The virtual world will always be accessible and personalised. You can change it by adding new virtual buildings or other objects, and the changes will remain in place the next time you visit. The metaverse will rely on your user-generated content, your digital creations, and your personal stories (like social media today).
- Connection to the real world. In some visions of the metaverse, the virtual material duplicates the real one. For example, you can control a virtual drone in the metaverse to handle an actual drone in the real world. People talk about the real and the virtual as ” digital twins.”
Conclusion
Metaverse began with gaming: for example, it was a Travis Scott concert in Fortnite.
 The development of GameFi supported all this, an in-game economy built on the blockchain. Venture funds and private investors are now actively investing in all of the above industries, and the market is growing and gaining liquidity.
The development of GameFi supported all this, an in-game economy built on the blockchain. Venture funds and private investors are now actively investing in all of the above industries, and the market is growing and gaining liquidity.
Source: Kyros Ventures
No one knows what the final version of the “established” metaverse will look like. It is hoped that corporations seeking to build Metaverse will consider the experience of data leakage and be able to rebuild the format of work to a new one: without risks and consequences for users. Is it possible to “seamlessly” solve problems and mitigate the risks associated with data leaks and privacy? Who knows.
VR, NFT, and Metaverse are all tools. What matters is not where we exist but what we do. Technologies can push simulators into the virtual space, where there will only be fakes and a lot of advertising, or they can give absolutely everyone access to good education and remote work.
The future will come, whether we want it or not. The question is who we will be in this new future.


